Metaverse Explained: The Exciting Whole Story About The Immersive Virtual World

Quick menu
- Perspectives on Metaverse
- The Metaverse’s Characteristics
- The 7 layers of Metaverse by Jon Radoff
- 9 Megatrends that are shaping the Metaverse
- Brands with Metaverse presence
- Devices that are used to enter Metaverse
- Top Companies that are developing the Metaverse
- Conclusion with Web 3.0
Trillions of dollars: that’s how much private industry is investing into the metaverse.
To begin, let’s define the metaverse. The meaning of the metaverse is up to interpretation and can be used to describe a variety of experiences. A virtual reality headset may transport you to the metaverse, which is a complete virtual universe. However, through a more mobile digital overlay, the metaverse can also be integrated into the world around you. Pokémon GO has lately brought this augmented reality-based approach to a wider audience.
The term “metaverse” was first used in Neil Stevenson’s 1982 novel, Snow Crash. Stevenson’s metaverse was a virtual world where characters may escape from bleak totalitarian reality. Sega launched virtual reality arcade devices, such as the SEGA VR-1 motion simulator, in the early 1990s, which were popular in many arcades.
Perspectives on Metaverse
- The metaverse is a three-dimensional virtual reality environment in which users can interact with digital objects and each other in an immersive environment.
- The metaverse is a parallel universe to our own. However, it’s a universe that can collide with our own to produce immersive, interactive, and hyper-realistic experiences.
- The metaverse is decentralized, permanent, real-time, limitless, self-sustaining, and interoperable.
- The metaverse is a virtual world that integrates social networking, online gaming, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and cryptocurrency to allow people to connect digitally.
- People use the Internet to access the metaverse, which is a shared virtual environment.
- Mark Zuckerberg, the CEO of Facebook, believes that augmented reality glasses will become as common as smartphones.
- Blockchain is an integral part of the metaverse because the technology enables users to protect their digital assets in virtual reality through smart contracts.
- The metaverse is a hybrid of virtual, augmented, and physical reality that blurs the lines between online and offline activities. But, to put it another way, it’s a collection of platforms like the Sandbox, Mirandus, and Decentraland where people can connect in various ways.
The metaverse is still a work in progress, and it can be viewed as a fascinating experiment that is continuously surprising us. Companies and developers can come up with wildly different interpretations of the concept. Nobody knows what the future holds for the metaverse. You may, however, dive right in and watch the progress for yourself.
The Metaverse's Characteristics
The metaverse’s qualities will be discussed in this section of the metaverse guide. The metaverse is constantly evolving. As a result, when individuals log in, they can always expect to find new features and surprises. However, there are a few features that are present in all metaverse implementations. Different implementations may interact with these rules in various ways. However, you can rely on these central features for the most part in any metaverse version.
There Are No Boundaries or Limits
Without limitations or boundaries, the metaverse is necessary. There is virtually no limit to the amount of space available. It only requires correct implementation by metaverse-focused programmers.
There is no single authority in charge.
The metaverse isn’t like owning a single house or structure. It’s more akin to a huge plot of land inhabited by a diverse group of individuals. Deeds and proof of ownership are commonplace in the physical world. Blockchain-related systems are frequently used in the metaverse to showcase it.
It is never turned off and is always active.
Nobody can turn the world off. People can’t turn off the metaverse, either. It’s a decentralized system with numerous separate components. The metaverse does not exist on a single server.
It has a real-world-like functional economy.
In the metaverse, a working economy based on cryptocurrencies is expected. It will be used to purchase virtual land and things that are identical to those found in the real world. NFTs are used to safeguard digital assets that contain art. All of this allows for the purchase and sale of goods.
It offers a completely immersive sensory experience.
One or more senses are completely engaged by the metaverse. VR goggles are usually used for this. Audio cues are delivered via headphones, of course.
Real Social Connections Can Be Made
People can connect in the metaverse. Typically, these encounters take place with other people. However, even AI interactions can stimulate social interaction. People are always surprised by social interaction and can learn new things through conversing with others. This leads to metaverse economics and exploration.
Beamable chief executive Jon Radoff, who is also an author and game designer, has broken the metaverse down into 7 different layers: experience, discovery, creator economy, spatial computing, decentralization, human interface, and infrastructure
Layer 1: Experience
The metaverse is frequently pictured as a three-dimensional space. Users do interact with the metaverse in this manner, to be sure. Virtual reality goggles, for example, replicate three-dimensional worlds. Users can grip or move objects in those 3D environments using interface devices. The metaverse, on the other hand, is not a three-dimensional environment. It isn’t even a two-dimensional space.
Instead, the metaverse is a dematerialized reality with no regard for spatial dimensions. Alexa, for example, is embedded in little items that provide access to vast amounts of data. People in the metaverse can also travel across large swaths of virtual terrain that are ultimately reduced to the size of a hard drive.
People’s perceptions of spatial dimensions are dissolved in the metaverse. And it’s not limited to the metaverse. People can find components of the actual world inside the metaverse via the internet of things (IoT).
Layer 2: Discovery
The metaverse is a crucial layer that isn’t always easy to grasp. Exploration is more than just looking about in a virtual 3D world. Of course, this kind of investigation is a part of the metaverse’s larger experience. Many people like being the first to glimpse new vistas in the metaverse’s ever-changing surroundings.
However, the metaverse is more than just 3D surroundings, as previously stated. Inbound discoveries are part of discovery and exploration. Users will frequently come across community-created content, for example. Commercial interests will almost always be looking for people with similar interests.
Outbound exploration is possible within the metaverse. Outbound discovery would include things like adverts and what most people consider spam. However, there is a common thread running across all of these situations. They’re all about people in the metaverse having fresh experiences.
Inbound:
- Real-time presence
- Community-driven content
- N of your friends like App
- App stores (along with reviews, rating systems, and categorization/tagging)
- Curation — via featured application listings in stores, taste-makers, and “influencers”
- Search engines
- Earned media
Outbound:
- Display advertising
- Spam (email, LinkedIn, Discord)
- Notifications
Layer 3: Creator Economy
There is a full economy in the metaverse. As previously stated, the metaverse favors crypto currency-based blockchain exchanges. However, the economy of the metaverse is more complex than simply exchanging currency for products and services. A creator economy distinguishes the economy of the metaverse from that of the real world.
Both the early web and the metaverse went through two stages of growth. The first is the time of the pioneers. To develop digital content during this time, people needed a high level of knowledge. For example, to develop material for the early internet or metaverse, one would need to be an adept coder. The second, the engineering age followed, with new tools making content creation simple for even inexperienced developers.
The third is ultimately the creator era that defines a true metaverse. Ordinary people can make items here. They can also readily sell items.
Layer 4: Spatial Computing
The metaverse, as previously stated, tends to obliterate spatial dimensions. The digital and physical worlds are becoming increasingly blurred as the metaverse grows. What exactly is the difference between virtual and real? It’s simple to dismiss the digital world as unreal. But what if you have your money, one-of-a-kind items, and even real estate on the internet? This takes on a whole new meaning. A virtual reality room, for example, may have little to do with the physicality of the area.
Meanwhile, virtual worlds can mimic 3D environments. You can take virtual walks and observe real-world impacts. You’ll cover virtual miles, burn calories by moving your legs or arms, and simply feel at ease when gazing out at faraway horizons.
In some ways, you aren’t traveling a long distance in analog terms. You could be walking in place or down a narrow path. However, it is the sensation that counts.
Layer 5: Decentralization
A single entity or component that manages a completely digital system is referred to as centralized computing. This is the most straightforward method for creating and utilizing networks. End-users, on the other hand, do not have much control or freedom. Decentralized development is instead used in the metaverse. This means that the metaverse is made up of many different components that are all owned and created by different people.
Decentralization takes on several forms depending on how it is implemented. Interoperability, on the other hand, is a critical component of all parts of the metaverse. People design pieces that are compatible with one another using standards. This simply means that parts can be removed and replaced. This is analogous to removing RAM from a computer and replacing it with RAM from a different manufacturer.
To deal with things like blockchain, the metaverse employs shared standards. People can also develop their extensions or apps.
Layer 6: Human Interface
The extent to which people connect with technology is frequently underestimated. A smartphone, for example, is more of a supercomputer with a powerful network behind it than it is a phone. These gadgets also have a variety of sensors as well as some modest AI to facilitate interaction. And practically everyone uses it without giving it much attention during the day.
Smartphones aren’t just getting smaller and easier to use; they’re also becoming more powerful. They’re also included in metaverse interface devices. The Oculus Quest, for example, is effectively a VR-phone hybrid. The process of efficiently integrating components results in a human interface into the metaverse. Cyborgs are becoming more common.
Everyday household products are becoming smarter as a result of the internet of things. Smart glasses, for example, provide a new set of capabilities. The trend of people wearing new sensors on their bodies is predicted to continue.
Layer 7: Infrastructure
Finally, the metaverse is reliant on a sophisticated infrastructure. This is frequently thought of as a hazy system. However, most individuals are familiar with the metaverse’s components. Because of their regular usage of mobile phones, for example, everyone is familiar with wireless networks. 5G networks will do more than increase call quality. It also provides faster data transmission. This increases people’s ability to access the data-rich metaverse.
Mobile devices’ improved capabilities allow for a better user interface. It also makes it easier to build VR and other display devices with small form factors. The Oculus Quest demonstrates that manufacturers may design systems that incorporate mobile components and virtual reality technology.
The large-scale convergence of characteristics between many technologies aids the metaverse’s infrastructure development. As the metaverse develops, more people will be able to access it.
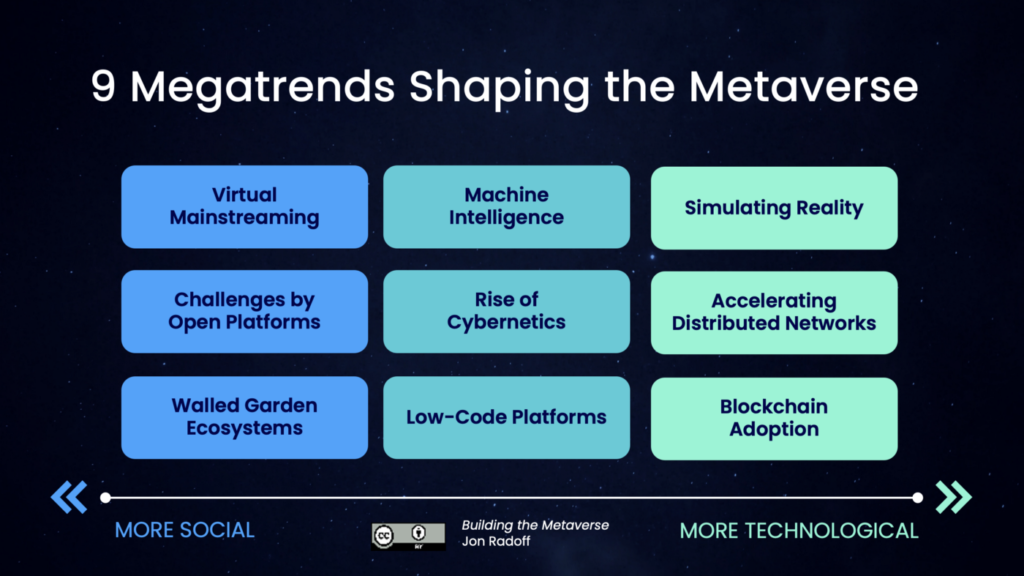
9 Mega Trends That Are Shaping the Metaverse At Global Scale
Jon Radoff in his article “9 megatrends shaping the metaverse” details about the exponential shifts that are underway at the global scale, that will shape the metaverse.
- Virtual Mainstreaming And The Changes it brings to Society
In the physical world trust is the foundation on which the entire framework of relationships, businesses, and legal systems operate which is scalable. No in the virtual realm, it is online friends, virtual items and crypto assets, smart contracts, and live online experiences which is scalable when industries support it.
These trends have their counter-trends. As people value the virtual world more, when they believe virtual relationships and property to be real, there will be more cybercrime, online bullying, abuse, cheating in games, and cheating in relationships.
The solution lies not in technology or products but in value-based education, training, virtual literacy, supportive communities, and understanding parents.
- Low-code Platforms That Will Democratise Metaverse
Applications in low-code and no-code application platforms (LCAP) with
high-level abstractions (such as visual scaffolding and drag-and-drop tooling) are used to replace hand-coding of processes, and logic.
Gartner forecasts that by 2023, over 50% of large enterprises will use LCAPs to operate at least part of their infrastructure.
The automation of workflow, deployment, security, scaling, and integration with numerous data endpoints accounts for a substantial portion of LCAP’s “magic.” The majority of the time spent developing Internet applications is spent on this complexity and scale.
The most obvious advantage of this development is that non-programmers can now perform some of the tasks that previously required programmers. There will be a visible shift
- from who does the work to a massive reduction in the quantity of work required to create applications,
- developers moving toward a serverless architecture
- an expanding number of creator tools that make it simple to produce metaverse content, script sophisticated behaviors, and engage in commerce.
Machine Intelligence
Machine intelligence will be integrated into our no-code and low-code application platforms, where it will act as a service architecture and design advisor. The transformation is that it will
- impact creativity, as computers become collaborators in the creative process
- AI will be utilized to create the metaverse’s microchips and to generate code to help programmers.
- Machines will discern emotions, understand movements, and even predict where our eyes will look.
- Rise of Cybernetics and its Contribution to Metaverse
Cybernetics is about the integration of human sensory and motor systems with computers. Miniaturization and high-speed networking have brought supercomputers to our pockets. Devices like VR Goggles and smartphones, which are becoming archaic now, their technology will merge and will pave the way for Oculus-like devices from Facebook. These wearable spectacles with cameras are responsive to our eyes, head position, and gestures and bring this experience to more of the world surrounding us.
Devices are getting closer and closer to the body. For example, the Light Field Technology which is used in smart contact lenses creates a holographic experience that will increasingly interpret our voice instructions, our gestures, and our biometrics. And neural interfaces may even allow our devices to understand our intentions.
The metaverse will be more than just a location we visit. We will be surrounded by the metaverse.
- Challenges by Open Systems and Open Platforms
Thriving days for Open Systems like Linux and PC in the future. Open Source and open platforms are a social phenomenon, more democratic, and permissionless, allowing widespread collaboration between software engineering projects, creating more value than all permissioned platforms combined. Some trends
- WebAssembly (Wasm) claims to provide sandboxed binary programmes for the open web that are fast and secure.
- WebGL and WebXR will aid in the creation of graphical and immersive experiences that can be distributed outside of app stores.
- Platforms like Unity Data-Oriented Technology Stack (DOTS) are leveraging these platforms to deliver compact, efficient binaries that perform at the level the metaverse requires.
- Revolutionary changes with Blockchain Adoption
Because you don’t have to trust anyone’s authority, blockchains, decentralized ledgers, or universal ledgers, are referred to be “trustless” systems.
Decentralized authority, a record of history and provenance, and demonstrable scarcity of assets are all possible with blockchains. A decentralized blockchain allows for permissionless participation or governance via a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO).
Since programmability is inherent in blockchains, it is used in building Etherium and smart contacts. Just like a network system, the more the nodes, the more the participation and so more the value of the network, where groups can form activities like games, financial legos, etc. Now here this trustless smart contract’s value contribution is exponential since more individual participates creating more applications and more value making it socially scalable.
Decentralized loans, decentralized finance, and decentralized asset exchanges have all been made possible via network effects. The advent of non-fungible assets may form the basis of virtual products in a new generation of games, avatar modifications, and metaverse experiences, while the emergence of blockchain computing may replace some components of cloud computing.
When assets, data, and programmable contracts are released into the open Internet, this is just the beginning of the possibilities.
The Business of Walled Garden Ecosystems
The ecosystem operator controls all operations in a Walled Garden. Here users are given a limited collection of technology or media information to create a monopoly or secure information system.
The Horizon, Metaverse from Facebook, can be called a Walled Garden whereas Decentaland can be an Open ecosystem.
Walled gardens aren’t a problem. The problem is that there are too few walled gardens. It should be simple for you to design your walled garden and ask other creators to join in, add to, change, and link it according to your rules.
- Accelerating Distributed Networks Technology Growth
Accelerating speeds are required to sustain the metaverse, but it is the network effects that occur when all network users can share real-time data that provide the most intriguing applications. Because the local network layer is no longer the bottleneck, the focus will shift to bringing greater computing power to the network’s “far” edge.
- The impact of Simulating Reality
- Ray tracing simulates how images appear, depending on how photons bounce between and across various materials by using the physics of light. Ray tracing can produce significantly more beautiful and realistic graphics, which is why it is employed in pre-rendered content like movies, but it necessitates a significant increase in computing power. What if it is in real-time.
- NVIDIA’s Omniverse platform is performing simulated fluid dynamics
- Consider being able to show a river or an HVAC system with great accuracy
Imagine all of these simulations and AI engines being connected to an interoperable framework that enables logic and prediction to mimic a world of virtual machines, objects, places, and people.
Jon Radoff says,” We won’t simply have an Internet of Things — we’ll have an Internet of Everything — integrated with predictive analytics, AI, and real-time visualization.”
Brands with Metaverse presence
Why are established businesses so eager to become metaverse brands? One of the most compelling reasons is that the metaverse can effectively serve as a virtual replica of reality. Products sold in brick-and-mortar establishments can be duplicated for people all over the world. This eliminates geographical barriers to prospective sales immediately.
Customers can test digital objects in a completely 3D environment. Friends can also come along to share their impressions of a new look thanks to the metaverse’s social component.
Here are the brands to experience in Metaverse.
Zara
Zara is a Spanish clothing company that has collaborated with Ader Error, a South Korean fashion collective, and Zepeto, a South Korean app, to enter the digital fashion sector. By making virtual apparel and make-up available to the app’s configurable avatars, the idea hopes to identify the new generation based on their individuality. This indicates that the company approaches fashion in a unique and high-tech way.
Zara’s perspective on metaverse consumer brands exemplifies one of Web 3.0’s key features. Zara ensures that customers may seamlessly shift from the physical to the virtual worlds of buying. Their clothing line, for example, features distinct black, yellow, bright orange, and navy blue palettes and is available in both physical and digital formats.
Nike
Nike is a well-known sports and fitness brand that emphasizes fun and competitiveness, as well as one of the most widely recognized consumer brands in the metaverse. Within the Roblox system, Nike has one of its most important metaverse projects.
Nikeland was intended to assist people in incorporating sports and recreation into their daily lives. Parks, courts, obstacle courses, and running tracks can all be found there. All of this has been meticulously built as a metaverse brand to demonstrate what Nike is all about. In addition, gamers can buy digitalized Nike things, such as clothing and shoes, to further their relationship with the company. Nike has developed several mechanisms for consumers to interact with its ethos in the metaverse.
Burberry
Burberry is a luxury fashion house recognized for its high-end offerings. However, after cooperating with the game designers of Honor of Kings, the brand has now ventured into a whole new area of fashion. Burberry’s apparel was included in the cooperation. A trench coat, boots, crop top, and shorts make up the most prominent item.
A crystal-embroidered vest, bib-front pants, a blue trench coat, and wader boots are also available from the brand. One of the unusual twists is that the entire ensembles as well as individual selections are accessible both online and offline. This is the type of convergence that has drawn people to metaverse brands.
Forever 21
Forever 21 debuted its first store in 1984, and now it’s expanding into the metaverse. It’s currently one of the Roblox consumer brands. However, Forever 21 takes a different approach. Rather than operating a single store, they are allowing consumers to construct their own. Users can build the decor of a Forever 21 store and even hire non-player character employees.
Forever 21 also maintains a high level of consistency between its metaverse and real-world products. When the business launches a new collection in the real world, it will be available on their Roblox sites as well. Forever 21 also offers themed districts where users may easily share avatar photos.
Vans
Vans is widely regarded as one of the original and most important brands in the action sports industry. They’re also one of the most well-known metaverse brands nowadays. Vans leaped with the release of “Vans World,” a Roblox-based interactive experience.
Vans World allows consumers to try out the brand’s products in a virtual environment that closely resembles what they’d find in the real world. Skateboarders, for example, adore Van’s footwear. Vans World also has a full skate shop as well as areas where you can practice kickflips, ollies, and any other trick. It allows users to do more than just examine how different products may appear on them. Users can also get a taste of the Vans lifestyle.
Ralph Lauren
Ralph Lauren has become a fashion icon in the United States. As a result, the announcement that they will be expanding into the digital world caused quite a stir among metaverse brands. Ralph Lauren’s metaverse services are created particularly for Roblox and include themed events. Users can participate in winter-themed activities through the Ralph Lauren Winter Escape experience, for example. Toasting marshmallows, drinking coffee, and ice skating in a winter wonderland was all part of the festivities. In the meanwhile, viewers can peruse the Ralph Lauren Digital Collection for a taste of retro fashion inspired by 1990s trends. Avatars can dress up in Ralph Lauren’s archived sportswear.
Tommy Hilfiger
User-generated content is common among metaverse brands, but Tommy Hilfiger stands out for actually honoring the role of those who use their products. Tommy Hilfiger has created a “Tommy x Roblox Creators” collection in collaboration with user-generated content (UGC). The collection consists of 30 digital fashion items that may be used within the Roblox platform and are inspired by the essential brand looks. Tommy Hilfiger has been outspoken about his involvement in the project. He mentioned how this collaboration allows people to put their creative spin on the official brand’s look. The younger generation of the established fashion brand might be more interested in this collaborative experience.
Balenciaga
One of the most well-known luxury houses in France is Balenciaga. Their products have a surreal quality to them. As a result, it shouldn’t come as a surprise that they’re one of the metaverse brands collaborating with Fortnite. Some Fortnite characters will be dressed in Balenciaga’s iconic looks as part of the relationship. A Balenciaga x Fortnite hoodie, cat-eye sunglasses, and boots are included in these “fit sets.”
Users can also purchase items from a Fortnite-based virtual Balenciaga store. They have a lot of fashion flexibility. The company has also created a “dynamic lookbook” that cycles from user-generated content and standard billboard pictures.
Devices that are used to enter Metaverse
Headset for VR (VR)
Virtual reality headsets are like high-tech goggles that sit over your eyes. The digital representation of the metaverse VR is displayed to each of your eyes. The headset also tracks head movement, so your vision changes in the virtual environment as you gaze about, much like it would in real life. The Oculus Quest 2 headset is available from Meta, formerly Facebook. Horizon Worlds, a brand-new Facebook metaverse app, is also available via Meta. Playstation VR is available for purchase from Sony. The Hololens metaverse headset from Microsoft is the most expensive but also the most capable.
AR Equipment
In the same way that virtual reality gear adds digital images to our perception of the world, augmented reality gear does the same. The fundamental distinction is that virtual reality completely replaces our vision of the world with a digital one. Instead, AR gear adds digital aspects to our existing vision of reality. AR gear is usually more expensive because it relies on two different parts. To allow you to roam around the world freely, AR has to be less cumbersome. Because larger pieces of equipment do not limit your movement, it also has to track your whereabouts more closely.
Gaming Console
You might be astonished to learn that you already have the metaverse’s central component in your living room. The Xbox does not support virtual reality or augmented reality. It does, however, offer Roblox and an interactive “metaverse museum.” If you own a Playstation, you can use the Playstation VR headset to access VR features. Sony was a pioneer in metaversal ideas. For the Playstation 3, Playstation Home offers cutting-edge advancements. Because PlayStation VR is such a compelling platform for metaverse development, anticipate Sony to take similar steps forward.
Computer
Because of their configuration, computers are one of the most effective ways to access metaversal systems. Computers are the most powerful, but also the most difficult to use. PCs run the majority of metaverse-accessing software. It is important to remember, however, that not all computers have the same configuration. The geography of a virtual environment requires a powerful GPU (graphics processing unit). To use with your PC, you’ll also need to get a VR or AR system. For transactions within a metaversal system, you could even need to set up a crypto wallet.
Mobile
Axie Infinity, for example, is a single-platform metaverse software. Roblox, on the other hand, is available for Android, iOS, and a variety of other devices. You can enter a virtual world with your smartphone running iOS or Android. Roblox is also compatible with both VR and non-VR systems. This implies you can utilize the same platform on your phone as folks using dedicated home PCs with complicated settings. Roblox is also a good place to start because you can always improve your hardware while staying in the same software portal.
Top Companies that are developing the Metaverse
This section of the metaverse guide contains examples of companies that are responsible for a large part of the metaverse’s development. The metaverse is largely a collective endeavor. Individuals and larger corporations contribute their skills and resources to ensure that the metaverse grows. However, some businesses stand out for their contributions. The companies listed below have made important contributions to the internet.
Meta
Facebook is a social networking site that allows people to engage with one another, form communities, and socialize from the comfort of their own homes. The social networking platform has broken down national barriers, allowing people from all around the world to engage.
Facebook has already renamed itself Meta and is testing metaverse technologies. Meta’s goals include creating 3D workrooms, virtual workplaces, and augmented reality headsets, among other things.
It has great ideas for its metaverse ambitions, such as Horizon workrooms, where individuals may meet virtually. It also produces virtual reality headsets and does research into other universes.
Roblox
Roblox is a 2004 American gaming startup. Roblox, an American gaming platform and game development studio is concentrating on creating metaverse environments.
Roblox has a large number of games, such as Meepcity and Bloxburg, that allow players to create virtual homes and conduct basic survival chores in the virtual world, such as obtaining a job and seeking adventure.
Roblox is concentrating on creating a metaverse platform where users can do more than simply play games. In the meta world, users may try on new outfits, build homes, talk with friends, and even go on adventures.
The basic goal of Roblox is to build a social platform where individuals can interact. Roblox hopes to provide 3D virtual experiences that are as realistic as possible. Roblox has just launched a new feature dubbed “spatial voice chat.” People will be able to voice communicate in three dimensions (the way people do in real life).
According to Roblox, voice talks will be akin to real-life conversations, and this feature is Roblox’s first move toward the metaverse. It also included “metaverse layered clothing,” which allows users to try on various layers of apparel on their digital avatars.
Epic Games
Epic Games was started in 1991 as an American video game and software developer. Fortnite, Unreal Engine 4, and Unreal are among the company’s most popular games. Survival games like Fortnite and Unreal Engine 4 appeal to thrill-seekers.
In addition, the corporation is on top of the metaverse race. Its primary goal is to create a metaverse platform where people can communicate with one another, interact with brands, and even extend their stay in the virtual world.
The metaverse portal will serve as a one-stop-shop for digital humans. Epic Games is actively considering the concept of meeting people electronically while having a real-life encounter.
It won’t only be digital. People will socialize in the Epic Space over discussions rather than emoticons. This platform will be made more fascinating by the virtual gaming, retail, and dining experiences.
To emphasize their metaverse intentions, Epic Games just launched “Digital Humans” (metahuman creation).
People will be able to use the metahuman builder tool to create photorealistic and animated humans that can play games. In the virtual world, the animated humans will fend off wars.
Web 3.0
It’s not “a” metaverse. A multiverse is the Internet’s next generation. We will be surrounded socially and graphically by the numerous adventures in this place.
While there will be many proprietary (and very enjoyable) theme parks in the metaverse, the real physical natural beauty might excite more: a metaverse fueled by a thriving creator economy enabled by decentralization is the future.
So we are entering an era where way we socialize, work, and play will be transformed by the metaverse.